Term: Alabama
**Historical Background of Alabama:**
– Etymology: Named after the Alabama people, a Muskogean-speaking tribe.
– Pre-European Settlement: Mississippian culture thrived in Alabama from 1000 to 1600 CE.
– European Settlement: Alabama was part of French, British, and Spanish territories during the colonial period.
– Admission to the Union: Alabama was admitted as the 22nd state in 1819.
– Spanish Control and Territorial Changes: Spain controlled the western territory until surrendering to the U.S. in 1813.
**Alabama in the 19th Century:**
– Alabama Territory created in 1817, with St. Stephens as the capital.
– Population growth from under 10,000 in 1810 to over 300,000 by 1830.
– Cahaba served as the first permanent state capital.
– Alabama Fever land rush attracted settlers for cotton cultivation.
– Civil War and Reconstruction: Alabama seceded from the Union in 1861.
**Civil Rights Movement and Modern Changes in Alabama:**
– Civil Rights Movement: Events like Montgomery bus boycott and Voting Rights Act of 1965.
– Population Shifts: Industrial development during World War II led to urbanization.
– Voting Systems: Implementation of new voting systems for increased representation.
– Economic Shifts: Decline of traditional industries and growth of technology and manufacturing.
– Modern Changes: Redistricting in 1972, changes in voting systems, and economic shifts.
**Geography, Climate, and Natural Disasters in Alabama:**
– Geography: Alabama’s size, landscape, and notable natural wonders.
– Climate: Humid subtropical climate with details on temperature and rainfall.
– Tornadoes: Alabama’s vulnerability to tornadoes, especially in the northern region.
– Weather: Details on winters, snowfall, and temperature extremes.
– Flora and Fauna: Diverse plant and animal species in Alabama’s habitats.
**Population Statistics and Recent Events in Alabama:**
– Population: Alabama’s population growth and demographics.
– Recent Events: Hurricane Ivan, 2011 tornado outbreak, and monument removal protests.
– 21st Century Events: Chief Justice Roy Moore’s actions and impact of natural disasters.
– Population Statistics: Foreign-born residents, center of population, and demographic trends.
– Alabama History: Disenfranchisement laws, Rosenwald Schools, and the Great Migration.
Alabama (/ˌæləˈbæmə/ AL-ə-BAM-ə) is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gulf of Mexico to the south, and Mississippi to the west. Alabama is the 30th largest by area and the 24th-most populous of the 50 U.S. states.
Alabama | |
|---|---|
| State of Alabama | |
| Nicknames: the Yellowhammer State, the Heart of Dixie, the Cotton State | |
| Motto(s): | |
| Anthem: "Alabama" | |
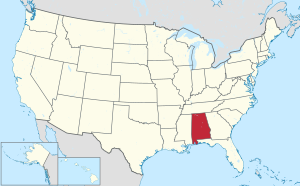 Map of the United States with Alabama highlighted | |
| Country | United States |
| Before statehood | Alabama Territory |
| Admitted to the Union | December 14, 1819 (22nd) |
| Capital | Montgomery |
| Largest city | Huntsville |
| Largest county or equivalent | Jefferson |
| Largest metro and urban areas | Greater Birmingham |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Kay Ivey (R) |
| • Lieutenant Governor | Will Ainsworth (R) |
| Legislature | Alabama Legislature |
| • Upper house | Senate |
| • Lower house | House of Representatives |
| Judiciary | Supreme Court of Alabama |
| U.S. senators | Tommy Tuberville (R) Katie Britt (R) |
| U.S. House delegation | 6 Republicans 1 Democrat (list) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 52,419 sq mi (135,765 km2) |
| • Land | 50,744 sq mi (131,426 km2) |
| • Water | 1,675 sq mi (4,338 km2) 3.2% |
| • Rank | 30th |
| Dimensions | |
| • Length | 330 mi (531 km) |
| • Width | 190 mi (305 km) |
| Elevation | 500 ft (150 m) |
| Highest elevation | 2,413 ft (735.5 m) |
| Lowest elevation | 0 ft (0 m) |
| Population (2020) | |
| • Total | 5,024,279 |
| • Rank | 24th |
| • Density | 99.2/sq mi (38.3/km2) |
| • Rank | 27th |
| • Median household income | $52,000 |
| • Income rank | 46th |
| Demonym(s) | Alabamian, Alabaman |
| Language | |
| • Official language | English |
| • Spoken language | As of 2010[update]
|
| Time zones | |
| Entire state (legally) | UTC– 06:00 (Central) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC– 05:00 (CDT) |
| Phenix City area (unofficially) | UTC– 05:00 (Eastern) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC– 04:00 (EDT) |
| USPS abbreviation | AL |
| ISO 3166 code | US-AL |
| Traditional abbreviation | Ala. |
| Latitude | 30°11' N to 35° N |
| Longitude | 84°53' W to 88°28' W |
| Website | alabama |
| List of state symbols | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
 | |
| Slogan | Share The Wonder, Alabama the beautiful, Where America finds its voice, Sweet Home Alabama |
| Living insignia | |
| Amphibian | Red Hills salamander |
| Bird | Yellowhammer, wild turkey |
| Butterfly | Eastern tiger swallowtail |
| Fish | Largemouth bass, fighting tarpon |
| Flower | Camellia, oak-leaf hydrangea |
| Horse breed | Racking horse |
| Insect | Monarch butterfly |
| Mammal | American black bear |
| Reptile | Alabama red-bellied turtle |
| Tree | Longleaf pine |
| Inanimate insignia | |
| Beverage | Conecuh Ridge Whiskey |
| Color(s) | Red, white |
| Dance | Square dance |
| Food | Pecan, blackberry, peach |
| Fossil | Basilosaurus |
| Gemstone | Star blue quartz |
| Mineral | Hematite |
| Rock | Marble |
| Shell | Johnstone's junonia |
| Soil | Bama |
| State route marker | |
 | |
| State quarter | |
 Released in 2003 | |
| Lists of United States state symbols | |
Alabama is nicknamed the Yellowhammer State, after the state bird. Alabama is also known as the "Heart of Dixie" and the "Cotton State". The state tree is the longleaf pine, and the state flower is the camellia. Alabama's capital is Montgomery, and its largest city by population and area is Huntsville. Its oldest city is Mobile, founded by French colonists (Alabama Creoles) in 1702 as the capital of French Louisiana. Greater Birmingham is Alabama's largest metropolitan area and its economic center.
Originally home to many native tribes, present-day Alabama was a Spanish territory beginning in the sixteenth century until the French acquired it in the early eighteenth century. The British won the territory in 1763 until losing it in the American Revolutionary War. Spain held Mobile as part of Spanish West Florida until 1813. In December 1819, Alabama was recognized as a state. During the antebellum period, Alabama was a major producer of cotton, and widely used African American slave labor. In 1861, the state seceded from the United States to become part of the Confederate States of America, with Montgomery acting as its first capital, and rejoined the Union in 1868. Following the American Civil War, Alabama would suffer decades of economic hardship, in part due to agriculture and a few cash crops being the main driver of the state's economy. Similar to other former slave states, Alabamian legislators employed Jim Crow laws from the late 19th century up until the 1960s. High-profile events such as the Selma to Montgomery march made the state a major focal point of the civil rights movement in the 1950s and 1960s.
During and after World War II, Alabama grew as the state's economy diversified with new industries. NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville would help Alabama's economic growth in the mid-to-late 20th century, by developing an aerospace industry. Alabama's economy in the 21st century is based on automotive, finance, tourism, manufacturing, aerospace, mineral extraction, healthcare, education, retail, and technology.
The state has diverse geography, with the north dominated by the mountainous Tennessee Valley and the south by Mobile Bay, a historically significant port. Politically, as part of the Deep South, Alabama is predominantly a conservative state, and is known for its Southern culture. Within Alabama, American football, particularly at the college level, plays a major part of the state's culture.